Customer Relationship Management Tools: Empowering Businesses with Efficient Customer Engagement sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. In a world where the customer journey shapes business success, CRM tools are the backbone behind every meaningful interaction and sustained relationship.
From their humble origins as physical ledgers to today’s advanced digital platforms, CRM tools have evolved into comprehensive solutions that centralize data, automate workflows, and offer actionable insights. Businesses now equip themselves with platforms that unify sales, marketing, and support, empowering teams to deliver personalized and efficient customer experiences. Understanding these powerful tools and how they drive engagement is the key to unlocking growth and ensuring your business stands out in a competitive landscape.
Introduction to Customer Relationship Management Tools
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools have become essential assets for businesses of all sizes seeking to foster lasting relationships with their customers. At their core, CRM tools are designed to centralize, organize, and manage a company’s interactions with both current and potential customers. By integrating various data streams and communication channels, these tools enable teams to deliver a seamless, personalized experience—helping businesses not only meet but also anticipate customer needs.
The primary purpose of CRM tools is to streamline processes related to sales, marketing, and customer service. By leveraging these platforms, organizations can track interactions across multiple touchpoints, automate routine tasks, and gain valuable insights from collected data. Over time, this structured approach enables companies to build trust, drive repeat business, and maintain a competitive edge.
Core Concept and Purpose of CRM Tools
CRM tools are designed to help businesses manage all aspects of their customer relationships from a single, unified platform. They serve as the digital backbone for storing customer information, tracking communication history, and managing sales pipelines, marketing campaigns, and support requests. These platforms also facilitate collaboration among teams, ensuring that everyone interacting with a customer has access to the latest information and can provide consistent service.
- Centralized Data Management: CRM systems collect and store detailed information about customers, such as contact details, purchase history, and preferences, making it easy for teams to access and update records in real time.
- Enhanced Collaboration: By offering a shared space for notes, documents, and conversations, CRM tools break down silos within organizations and encourage cross-functional teamwork.
- Automation of Processes: Routine tasks like follow-up emails, appointment scheduling, and lead scoring can be automated, freeing staff to focus on higher-value activities.
- Improved Customer Service: Quick access to comprehensive customer profiles enables support agents to resolve issues more efficiently and with greater personalization.
- Actionable Insights: Advanced analytics features help businesses identify trends, measure campaign effectiveness, and make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement.
Evolution and History of CRM from Manual to Digital Solutions
The journey of CRM began with simple, manual methods such as handwritten notes, Rolodex cards, and paper files. In the early days, businesses relied heavily on personal memory and fragmented systems, making it difficult to maintain consistent and reliable customer records. As organizations grew, so did the complexity of managing customer relationships, highlighting the need for more efficient solutions.
The 1980s saw the emergence of digital contact management software, which eventually evolved into Sales Force Automation (SFA) systems. These early tools helped sales teams track prospects, manage contacts, and schedule activities. By the 1990s, advancements in database technology and the rise of the internet spurred the development of more sophisticated CRM platforms, integrating marketing, sales, and customer support processes.
Today’s CRM solutions, such as Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics 365, are cloud-based platforms offering advanced features like artificial intelligence, omnichannel communication, and real-time analytics. They are now indispensable in modern business operations, capable of scaling alongside organizations and adapting to changing customer expectations.
Significance of Efficient Customer Engagement for Modern Businesses
Effective customer engagement is paramount in a competitive business landscape where customer loyalty can hinge on a single interaction. Companies that leverage CRM tools to engage customers efficiently experience higher satisfaction rates, increased retention, and greater lifetime value.
“In the digital age, efficient customer engagement isn’t just a competitive advantage—it’s a necessity. CRM tools empower businesses to understand, anticipate, and meet customer needs, transforming every interaction into an opportunity to build trust and drive growth.”
Key Features of Effective CRM Platforms

Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms have evolved into indispensable tools for businesses seeking to foster strong, long-lasting connections with their clients. The most effective CRM solutions are designed with a suite of features that streamline operations, centralize customer data, and drive efficient engagement strategies. This results in improved customer satisfaction, increased sales opportunities, and optimized team collaboration.
Modern CRM platforms deliver more than just a digital rolodex—they offer integrated workflows, actionable insights, and robust automation capabilities. The core features embedded in these systems empower businesses to nurture leads, close deals faster, and personalize every step of the customer journey. By leveraging these tools, organizations can respond swiftly to customer needs, track performance metrics, and build scalable client engagement models.
Essential CRM Features That Drive Business Success
The following segment introduces the foundational features that set effective CRM platforms apart. Each capability is tailored to address specific business needs—from managing customer information to automating repetitive tasks—enabling teams to focus on high-value activities.
| Feature | Benefit | Typical Use Case | Example Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Centralizes all customer information, ensuring easy access and comprehensive profiles. | Organizing leads, tracking communication history, and segmenting contacts by demographics or behavior. | Salesforce, HubSpot CRM |
| Sales Tracking | Monitors sales pipeline stages, forecasting revenue and identifying bottlenecks. | Visualizing deal progress, setting reminders for follow-ups, and analyzing conversion rates. | Pipedrive, Zoho CRM |
| Workflow Automation | Reduces manual work by automating repetitive tasks such as follow-up emails or task assignments. | Triggering welcome emails, scheduling meetings, or assigning leads based on rules. | Microsoft Dynamics 365, Freshsales |
| Reporting & Analytics | Provides actionable insights through real-time dashboards and custom reports. | Measuring team performance, evaluating campaign effectiveness, and identifying sales trends. | Insightly, SugarCRM |
| Omnichannel Communication | Unifies customer touchpoints—email, chat, phone, and social media—into a single interface. | Responding to support tickets, handling social media inquiries, and tracking all interactions in one place. | Zendesk Sell, Bitrix24 |
| Mobile Accessibility | Enables teams to access CRM tools and data securely from any location via mobile devices. | Managing leads, updating records, and staying connected with clients while on the go. | Zoho CRM, Salesforce Mobile App |
“Effective CRM platforms enable businesses to deliver personalized experiences, automate critical workflows, and make data-driven decisions—all from a unified system.”
Customization and Integration Capabilities for Diverse Business Needs
Every organization operates with its own unique processes, goals, and technology stack. Modern CRM solutions recognize this diversity by offering robust customization options and seamless integration with a wide range of business applications. These capabilities allow companies to fine-tune the platform according to their workflows and existing infrastructure, ensuring maximum efficiency and relevance.
Before exploring specific examples and best practices, it’s essential to understand why customization and integration matter in the CRM landscape:
- Custom fields and modules enable businesses to tailor data entry forms, dashboards, and workflows to mirror their unique sales cycles, support processes, or industry requirements.
- Extensive API support and pre-built integrations with tools like email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce systems streamline data flow and eliminate silos.
- Adaptable user permissions and role-based access ensure that sensitive information is only available to relevant team members, enhancing both security and productivity.
For example, a real estate agency might customize its CRM to track property listings, client preferences, and transaction milestones, integrating seamlessly with digital signature and document management platforms. Meanwhile, an e-commerce business could connect its CRM to order management and customer service systems, enabling a unified view of the customer journey from discovery to post-sale support.
By embracing these adaptable features, businesses of all sizes can future-proof their operations and respond proactively to evolving customer expectations and market trends.
Types of CRM Tools
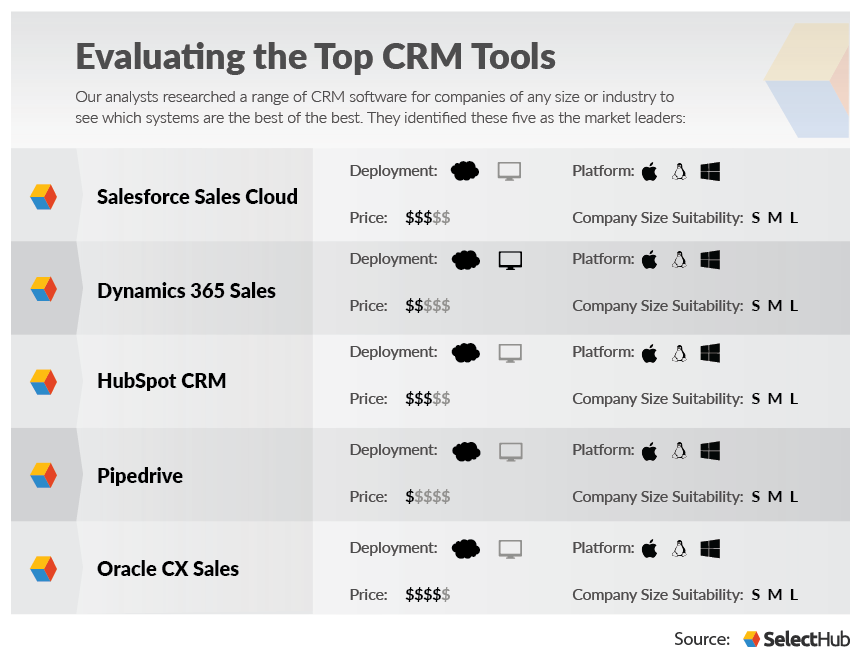
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools come in various forms, each designed to meet diverse business needs and technological preferences. Understanding the different types of CRM tools, from deployment models to system functionality and industry-specific applications, helps businesses choose the solution that best aligns with their operational strategies and growth objectives.
Modern CRM solutions can be classified based on how they are deployed, the core functions they offer, and their ability to adapt to specific industry requirements. This classification ensures that businesses can select a CRM platform that is not only technically suitable but also offers features tailored to their unique customer engagement goals.
CRM Deployment Models: Cloud-Based, On-Premise, and Hybrid
The way a CRM system is implemented significantly affects its accessibility, scalability, and maintenance. Below is an overview of the primary CRM deployment models:
- Cloud-Based CRM: Hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. These solutions are popular for their ease of deployment, automatic updates, and flexible subscription models. Salesforce and HubSpot CRM are leading examples.
- On-Premise CRM: Installed locally on a company’s own servers, offering complete control over data and customization. This model suits organizations with strict data privacy or regulatory requirements, such as large financial institutions.
- Hybrid CRM: Combines both cloud and on-premise elements, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of both models. This approach is often chosen by global enterprises needing both mobility and localized data control.
Choosing the right deployment model balances operational flexibility, security requirements, and budget constraints.
Operational, Analytical, and Collaborative CRM Systems
CRM systems can be further categorized by their primary focus, helping organizations streamline different aspects of customer management. Below is a comparison of the three core CRM types:
Each CRM system is designed to optimize particular business processes. The following table summarizes their key distinctions and benefits:
| CRM Type | Main Functionality | Key Benefits | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational CRM | Automates sales, marketing, and service processes to improve day-to-day interactions with customers. | Enhances efficiency, improves lead management, and supports service automation. | Managing sales pipelines, tracking customer support tickets, campaign management. |
| Analytical CRM | Collects and analyzes customer data to guide decision-making and strategy. | Provides actionable insights, customer segmentation, and predictive analytics. | Customer behavior analysis, churn prediction, targeted marketing efforts. |
| Collaborative CRM | Facilitates information sharing across departments and external stakeholders to unify customer interactions. | Improves internal communication and delivers consistent customer experiences across channels. | Unified communication centers, shared customer databases, multi-channel support integration. |
Operational, analytical, and collaborative CRM systems address distinct business needs, but many modern platforms offer integrated features from all three categories.
Industry-Specific CRM Solutions and Their Tailored Functionalities
Industry-focused CRM tools are developed to address the specialized processes, regulatory requirements, and customer engagement tactics of particular sectors. These tailored solutions can significantly improve usability and effectiveness by providing pre-built modules and workflows relevant to the industry’s challenges.
Below are notable examples of how CRM systems adapt to specific industries:
- Healthcare CRM: Focuses on patient relationship management, appointment scheduling, follow-up reminders, HIPAA compliance, and integration with electronic health records (EHR) systems. Solutions like Salesforce Health Cloud are designed to streamline patient engagement and healthcare provider coordination.
- Real Estate CRM: Offers property listing management, lead tracking, automated follow-ups, and client communication tools. Platforms such as Zoho CRM for Real Estate enable agents to nurture leads and manage property portfolios efficiently.
- Financial Services CRM: Provides tools for regulatory compliance (like KYC and AML checks), portfolio management, customer onboarding, and secure document storage. Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Finance is tailored to the needs of banking and investment companies.
- Retail CRM: Includes loyalty program management, POS integration, customer segmentation, and omnichannel marketing campaign tools. Shopify’s CRM integrations help businesses deliver personalized shopping experiences and targeted promotions.
Industry-specific CRMs deliver greater value by addressing the nuanced workflows, compliance standards, and customer expectations unique to each field.
Advantages of CRM Implementation for Business Growth

Adopting Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools marks a significant turning point for businesses aiming to enhance their customer engagement and drive sustained growth. By centralizing processes and information, CRM platforms offer a more unified approach to managing customer interactions, leading to improved efficiency and stronger relationships. These advantages not only foster loyalty but also empower teams to make more informed decisions that propel the company forward.
CRM implementation brings transformative benefits to modern businesses. From streamlining communications to increasing sales conversions and strengthening customer retention, the multifaceted impact of CRM tools cannot be understated. Below, we Artikel key aspects of how CRM solutions fuel business expansion and operational excellence.
Streamlining Customer Communications and Fostering Loyalty
A well-integrated CRM system provides a unified communication hub, making every customer interaction clear and consistent. This centralized approach reduces the risk of miscommunication and ensures each team member is equipped with the latest customer insights. Companies benefit from improved collaboration and faster response times, both of which play a crucial role in nurturing lasting customer relationships.
- Automated follow-ups remind teams of scheduled calls and emails, ensuring no customer query goes unanswered.
- Personalized outreach is made possible by accessible customer history, preferences, and past interactions, increasing engagement and trust.
- Integrated communication channels consolidate emails, phone calls, chats, and social media messages, minimizing the chance of overlooking important messages.
“Consistent, personalized communication builds trust and loyalty, turning first-time buyers into lifelong advocates.”
Examples of Improved Sales Conversion Rates and Customer Retention, Customer Relationship Management Tools: Empowering Businesses with Efficient Customer Engagement
The structured data and automation in CRM platforms allow sales and support teams to better target their efforts and respond to opportunities promptly. This results in measurable gains in both sales conversions and customer retention.
Illustrative examples of CRM impact:
- An e-commerce business utilizing CRM workflow automation saw a 20% increase in follow-up sales by sending timely cart abandonment reminders tailored to customer interests.
- A B2B software firm improved its lead-to-customer conversion rate by 15% after using CRM analytics to identify the most promising leads and tailor approaches accordingly.
- Retail companies using loyalty programs integrated within CRM platforms consistently report customer retention rates 10-25% higher than competitors lacking such systems (Source: Gartner, 2023).
“Strategic use of CRM data enables meaningful engagement, paving the way for higher conversion and retention rates.”
Centralizing Customer Information for Better Decision-Making
CRM solutions excel at bringing all customer data into a single, accessible location. This centralized repository eliminates data silos, empowering teams with a comprehensive view of each customer’s journey and preferences. Decision-makers, in turn, can craft more targeted marketing strategies and identify growth opportunities with greater confidence.
This centralization supports businesses in:
- Accessing real-time dashboards that offer insights into customer behavior, purchase history, and engagement trends.
- Segmenting customers based on detailed criteria, allowing for more precise marketing and service efforts.
- Reducing manual data entry errors, leading to more reliable analytics and forecasting.
“Centralized customer data is the foundation for agile, informed business decisions that drive sustainable growth.”
Methods for Successful CRM Adoption
A well-implemented CRM system can transform how a business interacts with its customers, but the success of CRM adoption depends largely on how teams are onboarded and how ongoing engagement is sustained. By focusing on effective strategies for user adoption, organizations can ensure a smoother transition, maximize ROI, and drive long-term business growth.
Ensuring a smooth rollout requires more than just technical deployment; it involves preparing teams, streamlining workflows, and fostering a culture that embraces digital transformation. Organizations that prioritize structured onboarding and continuous learning experience significantly higher CRM utilization rates and improved customer satisfaction metrics.
Strategies for Onboarding Teams and Fostering User Adoption
A robust onboarding process creates the foundation for successful CRM use. When employees understand the benefits and functionalities of a CRM system, they are more likely to integrate it into their daily routines, leading to higher productivity and data accuracy.
- Communicate the value: Clearly articulate how CRM adoption will benefit both the organization and individual users, with examples such as reducing manual work or providing better client insights.
- Involve key stakeholders: Include representatives from sales, marketing, customer support, and leadership in the selection and customization process to ensure the system meets varied needs.
- Map current workflows: Analyze existing business processes and align CRM features with those workflows to minimize disruption and create a seamless transition.
- Pilot programs: Launch the CRM with a small group or department first, using their feedback to refine configuration and training resources before a company-wide rollout.
- Provide user-centric training: Offer hands-on sessions tailored to different roles, utilizing real-life scenarios and data, to highlight practical benefits and boost confidence.
- Designate CRM champions: Appoint internal advocates or super-users who can support peers, answer questions, and share best practices throughout the adoption process.
“User buy-in and clear communication are critical components of any successful CRM initiative.”
Best Practices for CRM Implementation
Adhering to proven practices ensures that CRM projects remain on track, avoid unnecessary delays, and deliver measurable results. Each phase, from planning to post-launch support, contributes to overall project success.
An organized, step-by-step implementation plan minimizes risks and accelerates the path to value realization. Below is a recommended sequence for effective CRM deployment:
- Define clear objectives and KPIs aligned with business goals to measure CRM success and impact.
- Assemble a dedicated project team responsible for overseeing vendor selection, customization, and rollout.
- Conduct a comprehensive data audit to identify, cleanse, and migrate existing customer information into the new system.
- Configure the CRM to match your organization’s terminology, processes, and reporting requirements.
- Integrate the CRM with essential business tools, such as email clients, marketing automation, and ERP systems.
- Test the system extensively with end-users to identify potential issues and gather feedback for improvements.
- Deliver multi-format training sessions, including in-person workshops, online tutorials, and quick reference guides.
- Launch the CRM in phases, starting with core functionalities and expanding to advanced features as user proficiency grows.
- Establish ongoing monitoring and support mechanisms, including dedicated help desks and regular performance reviews.
Role of Ongoing Training and Support in Maximizing CRM Efficiency
Continued education and responsive support are essential for maintaining user engagement and adapting to new features or processes. As CRMs evolve, so do the skills and knowledge required to leverage their full potential.
Organizations with strong training programs report higher data quality, reduced resistance to change, and faster adaptation to system upgrades. For example, Salesforce and HubSpot customers who invest in continuous learning resources show markedly improved sales pipeline visibility and client retention rates.
- Schedule regular refresher courses to keep users updated on new functionalities and best practices.
- Offer a variety of support channels, including live chat, user forums, and detailed knowledge bases, to address user concerns promptly.
- Encourage peer learning by organizing workshops where employees share success stories and innovative uses of the CRM.
- Monitor usage analytics to identify areas where users struggle and provide targeted support or training interventions.
- Recognize and reward high adoption rates and creative use cases, fostering a positive culture around CRM engagement.
“Ongoing training transforms a CRM from a static tool into a dynamic driver of customer engagement and business growth.”
Integrating CRM with Other Business Systems: Customer Relationship Management Tools: Empowering Businesses With Efficient Customer Engagement
Seamless integration of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools with other essential business systems is fundamental for organizations striving to deliver unified customer experiences and maximize operational productivity. Such integrations connect the dots between marketing, sales, and customer support, ensuring that all team members have access to accurate, real-time information and can collaborate effectively. When executed thoughtfully, these connections empower businesses to break down data silos, reduce duplication of efforts, and create more personalized interactions throughout the customer journey.
When a CRM is integrated with other core platforms—such as marketing automation, e-commerce, helpdesk, and accounting solutions—businesses benefit from centralized data, automated workflows, and improved decision-making capabilities. This synergy not only enhances customer satisfaction but also enables organizations to respond more rapidly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Common CRM Integrations with Business Platforms
Integrating CRM systems with various business platforms supports streamlined processes and a holistic view of customer interactions. Below is an HTML table that highlights typical CRM integrations, outlining the type of integration, its primary benefits, and some challenges that organizations might encounter during implementation.
| Platform | Integration Type | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketing Automation (e.g., HubSpot) | Data Sync, Campaign Triggering | Unified lead capture, targeted campaigns, improved lead nurturing | Data mapping complexity, managing duplicate contacts |
| Sales (e.g., Salesforce Sales Cloud) | Bidirectional Data Exchange | Accurate pipeline visibility, streamlined quoting, sales forecasting | System compatibility, real-time synchronization |
| Customer Support (e.g., Zendesk) | Ticket Synchronization, Knowledge Base Access | Faster issue resolution, contextual support, better customer insights | Maintaining consistent data, handling legacy systems |
| E-commerce (e.g., Shopify, Magento) | Order & Customer Data Integration | Personalized offers, accurate order tracking, inventory management | Integration security, high data volume handling |
| Accounting & Billing (e.g., QuickBooks) | Invoice and Payment Sync | Automated invoicing, up-to-date payment status, financial reporting | Data privacy compliance, reconciliation errors |
“Seamless CRM integration brings together business functions, ensuring every team operates with the same customer intelligence for improved outcomes.”
Enhancing Operations with Data Synchronization and Workflow Automation
Centralizing data across integrated systems eliminates the inefficiencies caused by isolated information. With synchronized data, customer profiles are kept up-to-date regardless of which platform was used to make changes—be it a support ticket, a sales deal, or a marketing interaction. This reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, and allows staff to focus on high-value tasks rather than administrative work.
Automated workflows further enhance efficiency by triggering actions based on predefined criteria. For instance, when a new lead fills out a marketing form, the CRM can automatically assign the lead to a sales representative, trigger a personalized email, and update the sales pipeline. Similarly, when a customer makes a purchase, the system can instantly send a thank-you note, create a support case for onboarding, and update financial records.
- Automated lead handoff: Smoothly transitions prospects from marketing to sales with complete context and history.
- Real-time notification: Sales and support teams are alerted immediately about customer activity, improving responsiveness.
- Customer journey visibility: Every interaction is logged, allowing for continuous optimization of sales and support strategies.
- Error reduction: Automation reduces the likelihood of human error in repetitive processes such as data entry and order processing.
Organizations like Amazon and Adobe are recognized for leveraging deeply integrated CRM ecosystems. Amazon synchronizes purchase history, support interactions, and marketing preferences across its platforms, delivering highly tailored shopping and support experiences. Adobe integrates its CRM and marketing clouds to deliver consistent, relevant messaging at every touchpoint, powered by real-time data and automated workflows.
By aligning systems through CRM integration, businesses can react swiftly to customer needs and market changes, laying the groundwork for scalable growth and sustained customer satisfaction.
Measuring the Impact of CRM on Customer Engagement
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are most valuable when their impact can be clearly measured. By tracking the right metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can evaluate how CRM initiatives drive improvements in customer engagement. This assessment enables organizations to refine their strategies, demonstrate ROI, and ensure customer-focused growth.
A robust measurement framework empowers teams to understand the real-world effects of CRM-driven changes. It highlights where efforts are succeeding in deepening customer relationships and where further optimization is needed.
Key Metrics and KPIs for Customer Engagement Assessment
Metrics and KPIs play a pivotal role in quantifying the influence of CRM tools on customer engagement. They allow organizations to monitor performance, set benchmarks, and identify trends over time.
- Response Time: Measures how quickly customer inquiries are addressed, reflecting the efficiency of CRM-supported communication workflows.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Gathers feedback through surveys, providing direct insight into how customers feel about their experiences.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Assesses customer loyalty by determining how likely customers are to recommend the business.
- Customer Retention Rate: Tracks the percentage of customers who continue to engage with the business over a specific period, indicating sustained value delivery.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Estimates the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer throughout their relationship.
- Engagement Rate: Monitors customer interactions across channels, such as email opens, clicks, and social media activity.
- Issue Resolution Rate: Measures the percentage of customer issues resolved in the first interaction or within agreed service levels.
- Sales Conversion Rate: Evaluates how effectively leads managed through the CRM are converted into paying customers.
“Effective CRM measurement relies on actionable KPIs that are closely aligned with strategic business objectives and customer expectations.”
Performance Indicators Demonstrating CRM-Driven Engagement Improvements
Selecting the right performance indicators enables organizations to make informed decisions and showcase the tangible benefits of their CRM investments. These indicators facilitate ongoing improvement by linking CRM activities to customer engagement outcomes.
- Reduced Average Response Time: After implementing CRM automation in customer service at a leading e-commerce retailer, average response times dropped from 12 hours to under 2 hours, significantly boosting customer satisfaction scores.
- Increased Customer Retention: A telecom company used personalized CRM campaigns to improve customer retention rates by 10% year-over-year, leveraging timely communications and targeted offers.
- Higher Customer Lifetime Value: By analyzing CRM data, a SaaS provider identified upsell opportunities, resulting in a 20% increase in customer lifetime value over 18 months.
- Improved Net Promoter Score: Banking institutions using CRM-based customer feedback loops reported an average NPS increase of 15 points within a year, highlighting stronger customer loyalty.
- Enhanced First Contact Resolution Rate: Insurance companies integrating CRM with their ticketing systems saw first contact resolution rates improve by 25%, reducing escalations and operational costs.
Examples of CRM-Facilitated Business Outcomes
Illustrating the impact of CRM on customer engagement can be achieved with real-world business scenarios. These demonstrate the link between CRM-driven engagement and measurable business benefits.
| Industry | CRM Feature Used | Engagement Improvement | Business Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Automated Email Campaigns | Personalized recommendations increased repeat purchases | Repeat purchase rate rose by 18% within six months |
| Financial Services | 360-Degree Customer View | Agents accessed complete client histories instantly | Case resolution time reduced by 40% |
| Healthcare | Patient Journey Mapping | Tailored follow-ups improved patient adherence | Appointment no-show rates dropped by 22% |
| Travel & Hospitality | Real-Time Feedback Collection | Guests’ needs addressed during stay | Customer satisfaction scores increased by 13 points |
| Education | Automated Notifications | Students received timely updates | Engagement with digital learning tools rose by 30% |
Common Challenges and Solutions in CRM Usage
Implementing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools can transform customer engagement, but the journey is rarely without its difficulties. Businesses, regardless of size or industry, often face a range of challenges when integrating CRM systems into their daily operations. Navigating these obstacles with proactive strategies is key to unlocking the true value of CRM platforms and ensuring long-term success.
Understanding the root causes of CRM adoption issues, from data integration to user acceptance, is essential. By anticipating potential roadblocks and applying targeted solutions, organizations can maximize their CRM’s impact, foster smoother transitions, and maintain data integrity.
Frequent Obstacles Encountered When Deploying CRM Tools
Several recurring challenges can hinder the full realization of CRM benefits. These issues often arise during initial deployment but can persist if not addressed proactively. Recognizing these obstacles is the first step toward effective resolution and optimal system utilization.
- Low User Adoption: Employees may resist new systems due to comfort with familiar processes or skepticism about added value.
- Data Quality Issues: Inconsistent or inaccurate customer data can undermine CRM effectiveness, leading to poor decision-making.
- Integration Complexity: Difficulty connecting the CRM with existing software (such as ERP, marketing automation, or e-commerce platforms) can create information silos.
- Insufficient Training: Inadequate education on CRM features and workflows often results in underutilization.
- Lack of Management Support: Absence of leadership buy-in may cause weak enforcement and unclear priorities across teams.
- Customization Challenges: Off-the-shelf solutions may not align perfectly with unique business workflows, requiring further adaptation.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Handling sensitive customer information without robust safeguards can increase risks of breaches and regulatory violations.
Practical Solutions and Proactive Measures for Overcoming CRM Usage Challenges
Successful CRM deployments rely on a combination of strategic planning, comprehensive support, and ongoing evaluation. The following practical solutions help address the most common hurdles and pave the way for smooth adoption and continued effectiveness.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve users early in the selection and implementation process to foster a sense of ownership and ensure the system addresses real-world needs.
- Data Cleansing and Standardization: Regularly audit and update customer records before and after CRM implementation to maintain data accuracy.
- Robust Training Programs: Provide tailored, ongoing training sessions to build user confidence and enable mastery of key CRM features.
- Phased Integration Approach: Integrate CRM systems incrementally with other platforms, allowing for troubleshooting and gradual adaptation.
- Strong Executive Sponsorship: Encourage leadership to champion CRM initiatives, set clear objectives, and communicate the system’s value to the organization.
- Custom Workflow Design: Leverage CRM customization capabilities—or partner with vendors for advanced configurations—to align the system with existing business processes.
- Continuous Feedback Loops: Establish channels for users to report issues and suggest improvements, ensuring the system evolves with business needs.
“Effective CRM implementation hinges on a balanced focus between technology, people, and processes—each element is crucial for overcoming adoption barriers and achieving business goals.”
Ensuring Data Privacy and Security Within CRM Systems
Protecting customer data is a foundational aspect of CRM usage. Regulatory requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) require businesses to implement strict controls on data access, storage, and sharing. Failure to adhere can result in significant penalties and reputational damage.
The following table Artikels key measures organizations should implement to safeguard CRM data and maintain customer trust.
| Data Protection Measure | Description | Industry Example |
|---|---|---|
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Limits data access based on user roles, ensuring sensitive information is only visible to authorized personnel. | A financial services firm restricts access to personal financial data to senior account managers only. |
| Data Encryption | Applies encryption to data at rest and in transit, protecting it from unauthorized interception or breaches. | An e-commerce retailer uses end-to-end encryption for customer payment details processed through their CRM. |
| Regular Security Audits | Conducts scheduled reviews of CRM security protocols and system vulnerabilities. | A healthcare provider performs quarterly security audits to ensure compliance with HIPAA requirements. |
| Automated Backup and Recovery | Implements automatic data backup and rapid recovery solutions to prevent loss from system failures or cyberattacks. | A SaaS company schedules nightly CRM backups and tests recovery processes monthly. |
| Consent Management Tools | Tracks and manages customer consent for data collection and communication, supporting compliance with privacy laws. | A marketing agency integrates opt-in tracking within their CRM to manage email campaign permissions. |
Visualizing typical CRM security architecture, one might imagine a layered system: outer firewalls screen inbound connections, while encrypted data repositories are located within an internal network. User authentication, biometric access, and audit logs create multiple checkpoints to deter unauthorized activity. This layered protection, when combined with ongoing monitoring and policy updates, forms a robust defense against cyber threats.
“Prioritizing data privacy and security in CRM platforms is not just a technical requirement—it is a fundamental component of customer trust and long-term business sustainability.”
Future Trends in CRM and Customer Engagement Technology
The landscape of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is evolving rapidly, fueled by advanced technologies and the growing need for hyper-personalized customer experiences. As businesses strive to build stronger, more meaningful connections with their audiences, future trends in CRM center around intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and sleek, user-friendly interfaces. These emerging capabilities are not only enhancing operational efficiency but also empowering organizations to anticipate customer needs, deliver timely service, and foster higher engagement across every touchpoint.
Modern CRM platforms are integrating sophisticated tools that leverage artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and automation. These technologies are transforming how businesses manage customer data, predict behavior, and personalize communication in real time.
AI, Machine Learning, and Automation Transforming CRM Capabilities
AI and automation are reshaping CRM by introducing advanced functionalities that streamline processes and make data-driven decisions possible at scale. These innovations are enabling organizations to anticipate customer needs, automate repetitive tasks, and deliver personalized interactions efficiently.
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are now integral to many CRM systems, handling routine inquiries, qualifying leads, and providing 24/7 customer service without human intervention.
- Machine learning algorithms analyze customer data to uncover trends and predict future behaviors, allowing businesses to proactively address issues and tailor offerings.
- Automated workflow engines minimize manual data entry and follow-ups, reducing human error and freeing sales and service professionals to focus on high-value activities.
For example, Salesforce Einstein and Microsoft Dynamics 365 AI capabilities are being used by enterprises to score leads, recommend next best actions, and automate case resolutions, all based on historical and contextual customer information.
Predictive Analytics and Personalization Enhancing Customer Relationships
Predictive analytics is playing a crucial role in transforming raw customer data into actionable insights, which businesses use to deliver highly personalized experiences. Combined with AI, predictive analytics allows organizations to move from reactive service to proactive engagement.
- CRM systems now harness vast amounts of historical and real-time data to forecast customer needs, detect churn risks, and suggest tailored offers or content.
- Personalization engines create dynamic customer journeys, adjusting communications and recommendations based on individual preferences and behaviors.
- Leading brands like Amazon and Netflix use these technologies to anticipate what customers want before they ask, exemplifying how predictive analytics powers relevant, timely interactions.
“Delivering personalized experiences, powered by predictive analytics, has moved from being a competitive advantage to an essential expectation for customer-centric organizations.”
In retail, for instance, companies like Sephora use CRM-driven predictive analytics to recommend skincare products at optimal times, leading to higher conversion rates and increased customer loyalty.
Innovations in User Interfaces and Mobile CRM Experiences
As workforce mobility and remote engagement become standard, CRM vendors are investing in more intuitive interfaces and seamless mobile experiences. These advancements aim to empower users to access insights and engage with customers from anywhere.
The latest CRM platforms feature:
- Voice-activated commands that allow sales and support teams to update records, schedule meetings, or retrieve customer data hands-free, supporting efficiency for field agents and remote workers.
- Adaptive dashboards and widgets that provide a customizable, role-based view of critical information, ensuring that users only see the data and tasks most relevant to their objectives.
- Responsive mobile apps that mirror desktop functionalities, equipped with features like offline data access, push notifications, and in-app messaging for on-the-go productivity.
For instance, Zoho CRM’s mobile app offers geolocation features, enabling field sales representatives to plan visits, check in at customer locations, and log interactions in real time. Similarly, emerging gesture-based and AR-driven interfaces are being piloted to enhance in-person customer interactions and minimize friction in information retrieval.
“Mobile-first CRM solutions with intuitive, voice- and gesture-driven interfaces are redefining how, when, and where professionals engage customers and manage relationships.”
These interface innovations, coupled with robust security and seamless integration capabilities, are paving the way for a more agile, collaborative, and customer-focused future in CRM technology.
Last Recap
In summary, Customer Relationship Management Tools: Empowering Businesses with Efficient Customer Engagement are more than just software—they are strategic assets that redefine how companies interact with and understand their customers. With the right CRM in place, businesses can foster loyalty, streamline operations, and set themselves up for sustainable success in a rapidly evolving market. Investing in CRM is not just about keeping up; it’s about leading the way in exceptional customer engagement.
FAQs
What industries benefit most from CRM tools?
Almost every industry can benefit, but CRM tools are particularly valuable for sectors like retail, hospitality, real estate, financial services, and B2B enterprises where managing relationships and customer data is crucial to growth.
Can small businesses afford CRM solutions?
Yes, many CRM platforms offer tiered pricing and flexible plans tailored for small businesses, making it accessible for startups and growing companies to implement robust customer management without breaking the bank.
How do CRM tools improve team productivity?
CRM tools automate routine tasks, centralize customer information, and streamline workflows, allowing teams to spend less time on manual data entry and more time focusing on building relationships and closing deals.
Is it difficult to migrate existing customer data into a new CRM?
Most modern CRM platforms provide import tools and migration support, making it straightforward to transfer data from spreadsheets or legacy systems, though careful planning and data cleaning are recommended for a smooth transition.
What are the common signs that a business needs a CRM tool?
Growing customer bases, difficulty tracking interactions, missed follow-ups, and lack of centralized data are common indicators that it’s time to adopt a CRM solution.

